Hey everyone I am Hasnain Makada currently working as a Developer Advocate at Napptive where I explore the platform closely and educate the community about DevOps and its various tools
In this blog, I'm going to show you how you can manage your Kubernetes clusters via its inbuilt dashboard and not using the minikube(s) dashboard
Before starting.. these things need to be running on your machine
- Docker & Kubernetes should be running
- And minikube should be started, if you are using any cloud providers, set up your Kubernetes cluster on that
What is a k8s dashboard?
From official docs : Kubernetes dashboard is a web-based Kubernetes user interface. You can use Dashboard to deploy containerized applications to a Kubernetes cluster, troubleshoot your containerized application, and manage the cluster resources.
If you want to get an overview of the clusters running or if you want to create or modify any individual Kubernetes resources such as (jobs, pod, deployments) etc. You can do that with the dashboard as well as with the CLI
The Kubernetes dashboard also provides the state of the Kubernetes resources of your cluster and any error it may catch, Everything is provided to you. That's the beauty of its dashboard.
Getting Started with the GUI
I'm gonna tell you a step-by-step process with which you can set up the dashboard on your local machine, So let's get started...
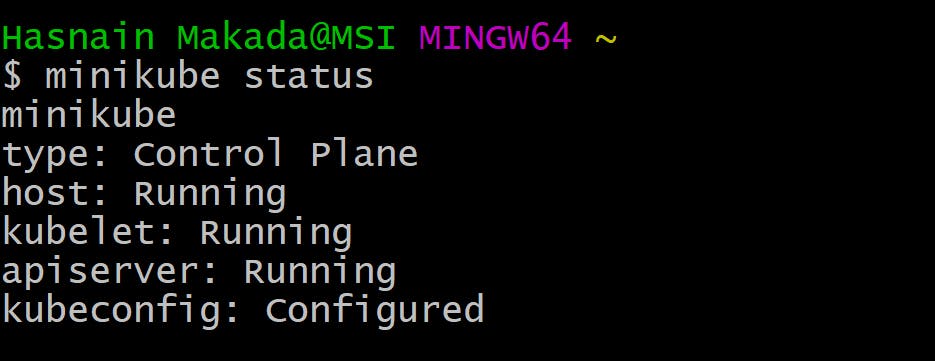
Step 1
Make sure that minikube is up and running by running minikube status in your terminal
Step 2
The Dashboard Ui is not deployed by default, To deploy it, run this command
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.6.1/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
It will take some time and apply all the necessary units required for the dashboard, if you're lens you can see them over here
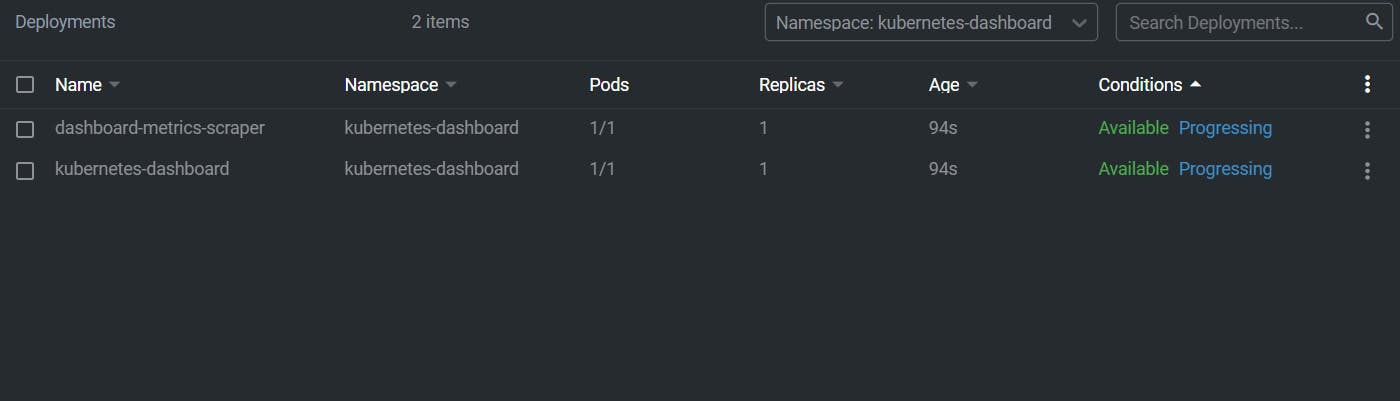
Step 3
Now that our recommend.yaml is applied successfully we're going to access the dashboard Ui, But before that keep in mind that the dashboard deploys with a minimal RBAC configuration by default and currently dashboard supports logging in with a bearer token, So for that, we're going to create sample user for accessing the dashboard
Create a new folder on the desktop or on your drive mkdir dashboard
Navigate to the folder created cd dashboard
Now we're going to create a file in which one will be a service account (granting admin services to the dashboard) and another will be a cluster-role-binding which will provide all the authorization to the admin-user which was created in the service account
Create a file name dashboard-adminuser.yaml inside the dashboard directory and print this service account and cluster-binding code inside it.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin-user
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
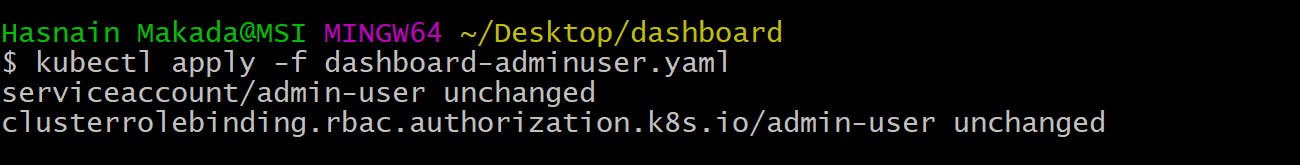
Now that you've successfully done the above part, Save the file and apply it to the k8s cluster kubectl apply -f dashboard-adminuser.yaml
It will display output like this,
Step 4
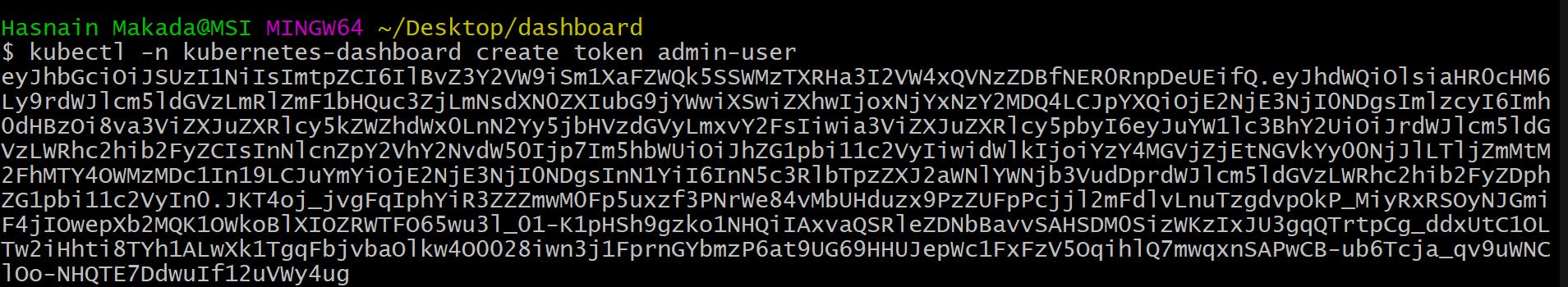
Now that we have successfully applied both things to our cluster, To access our cluster we will need a bearer token, To create a bearer token run
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard create token admin-user
It will print output something like this,
Step 5
Now that we have successfully generated the bearer token (The most imp. thing), Run kubectl proxy to access the dashboard
The dashboard will be available at localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes...
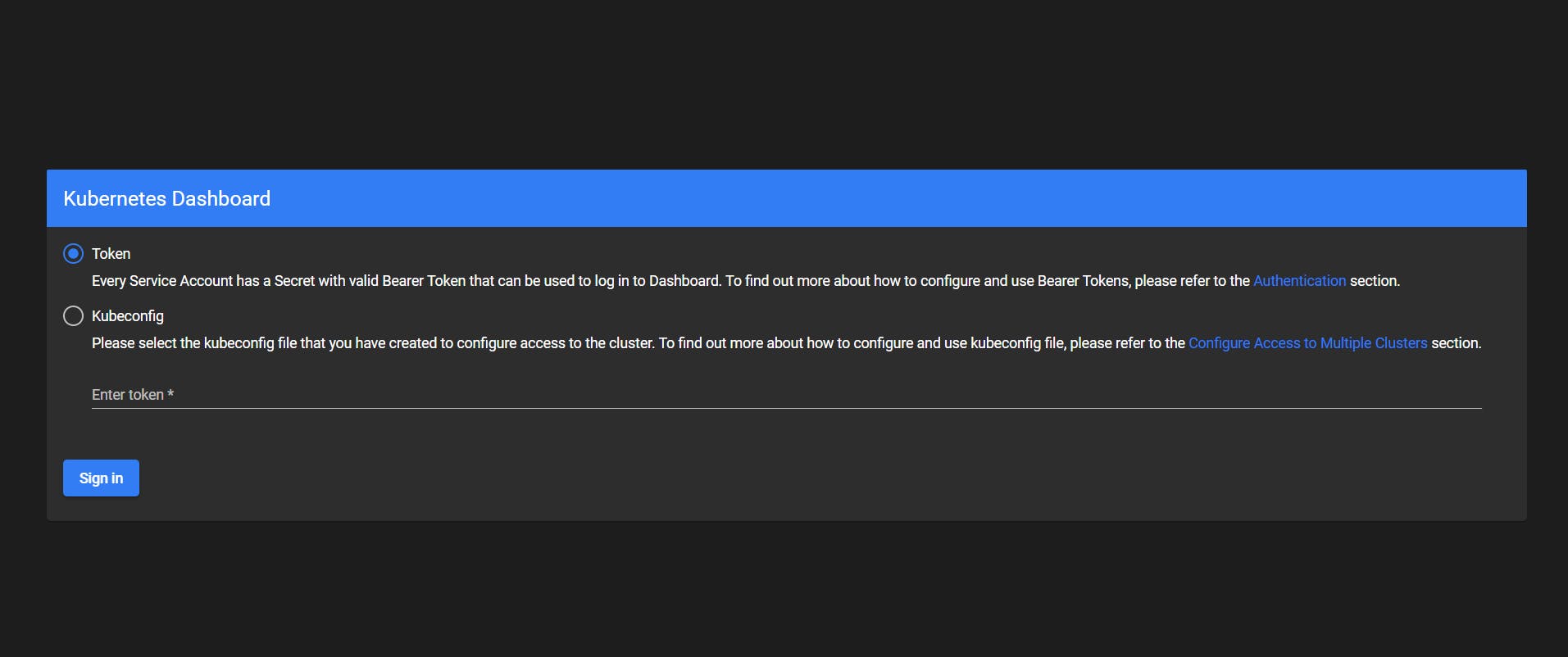
Now print the bearer token which we generated and you're good to go,
Let's test it !!!
So now that our k8s dashboard is up and running, Let's create a sample pod for testing. Create a sample-pod.yaml file and paste this simple code inside it.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-pod
labels:
name: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-pod
image: nginx:latest
resources:
limits:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "500m"
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Apply this pod to the cluster kubectl apply -f sample-pod.yaml -n default
Now locate to the dashboard,
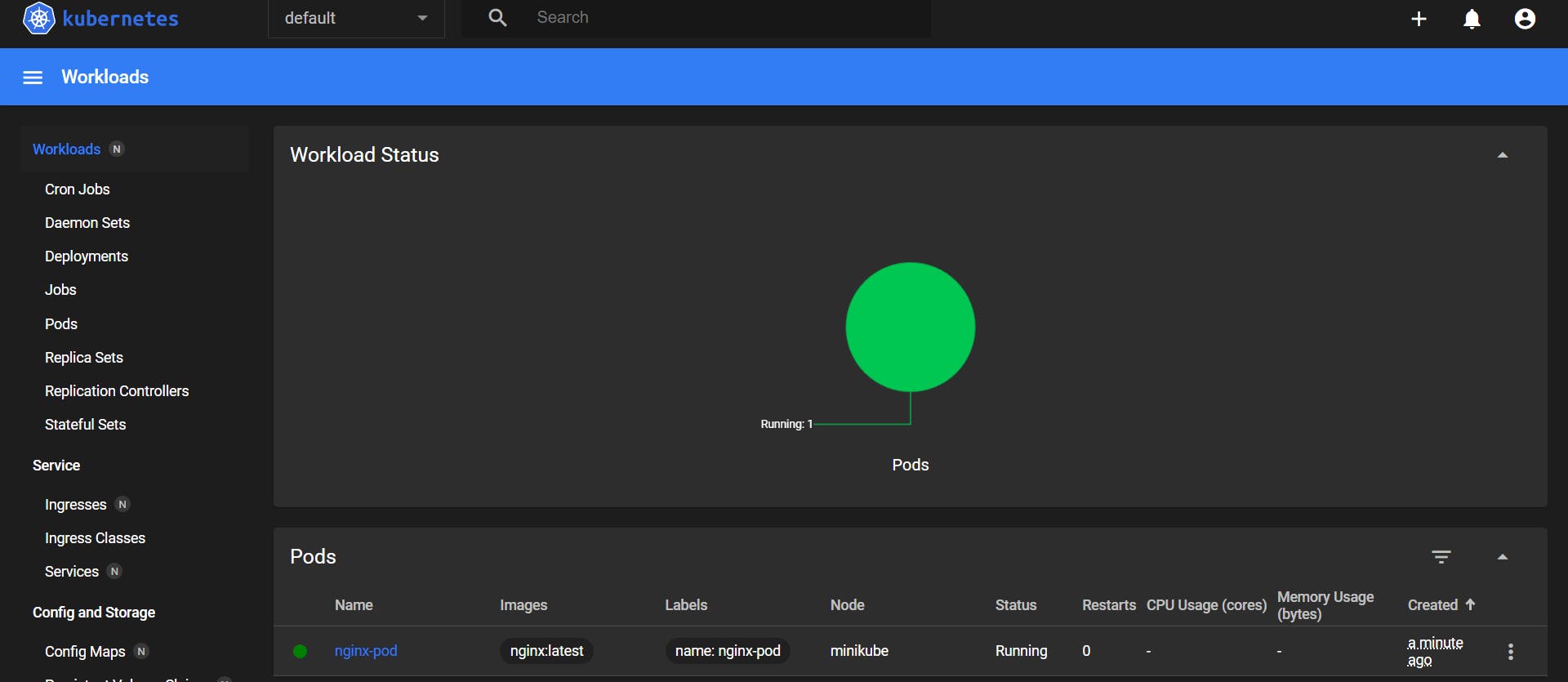
Now you can see your pod and manage it as per your choice
Conclusion
I hope that you now understood how to access k8s dashboard and how It can be useful while dealing with resources, If you have any doubts related DevOps & Flutter, feel free to reach me out on Twitter & showwcase

